Union Budget 2026–27: A Detailed, Investor-Focused Analysis

Introduction
Union Budget 2026–27 Analysis focuses on fiscal consolidation, infrastructure-led growth, manufacturing expansion, tax simplification, and long-term economic stability. The budget clearly signals that this is not a short-term trading budget, but a strategic roadmap for long-term investors, businesses, and policymakers.
Macro Snapshot: Fiscal Discipline with Growth Support
Key Fiscal Numbers (At a Glance)
| Indicator | FY 2025–26 (RE) | FY 2026–27 (BE) |
|---|---|---|
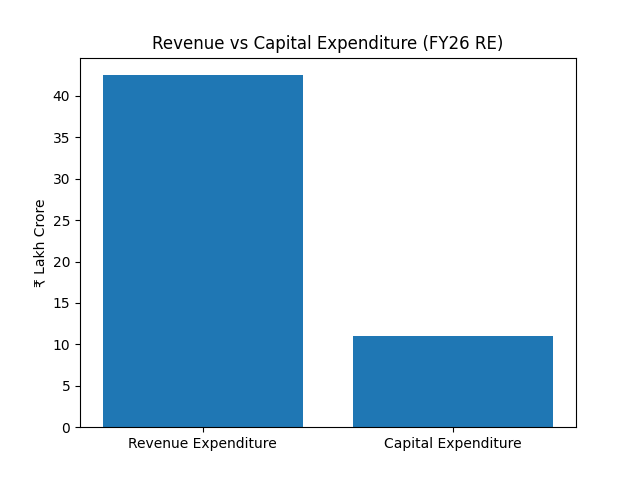
| Total Expenditure | ₹49.6 lakh crore | ₹53.5 lakh crore |
| Capital Expenditure | ~₹11 lakh crore | Sustained focus |
| Net Tax Receipts | ₹26.7 lakh crore | ₹28.7 lakh crore |
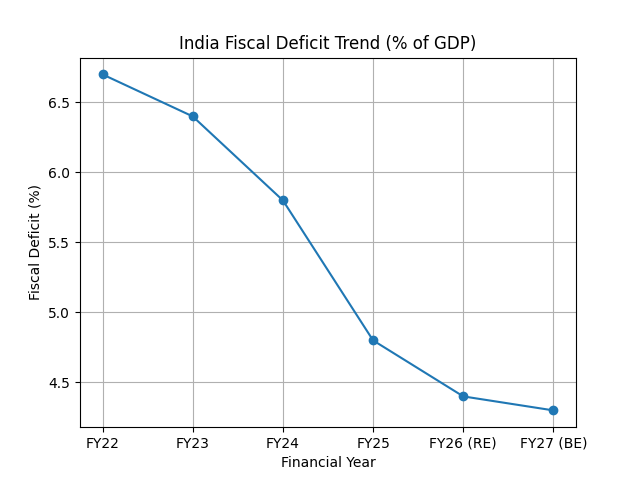
| Fiscal Deficit (% of GDP) | 4.4% | 4.3% |
Why it matters:
Fiscal deficit reduction aligns with India’s medium-term debt consolidation path
High capital expenditure supports long-duration growth and crowding-in of private investment
Infrastructure & Connectivity: Building Economic Corridors
High-Speed Rail & Urban Growth
7 High-Speed Rail Corridors announced as growth connectors
Introduction of City Economic Regions (CERs) focusing on Tier II, Tier III cities and temple towns
₹5,000 crore allocation per CER over five years (challenge-based funding)
Impact:
Real estate, cement, logistics, and urban infrastructure sectors stand to benefit
Balanced regional development reduces metro congestion
Manufacturing & Industrial Push: Strengthening Atmanirbhar Bharat
Key Schemes Announced:
Electronics Components Manufacturing Scheme outlay enhanced to ₹40,000 crore
India Semiconductor Mission (ISM) 2.0 – expanded to equipment, materials, and Indian IP
₹10,000 crore Container Manufacturing Scheme
Construction & Infrastructure Equipment (CIE) manufacturing support
Strategic Materials & Energy Transition:
Rare Earth Permanent Magnet Corridors in Odisha, Kerala, Andhra Pradesh & Tamil Nadu
Duty exemptions for lithium-ion cells, battery storage systems, solar glass inputs
Investment Insight: This signals long-term policy continuity for electronics, EV supply chains, renewables, and advanced manufacturing.
Agriculture & Rural Economy: Diversification Over Subsidies
Focus Areas:
High-value crops: coconut, cocoa, cashew, sandalwood, agarwood, nuts
Region-specific crop planning (coastal, hilly, North-East regions)
Revival of 200 legacy industrial clusters
Why this matters:
Encourages income diversification beyond staples
Improves export competitiveness and rural resilience
MSMEs & SMEs: Creating Future Champions
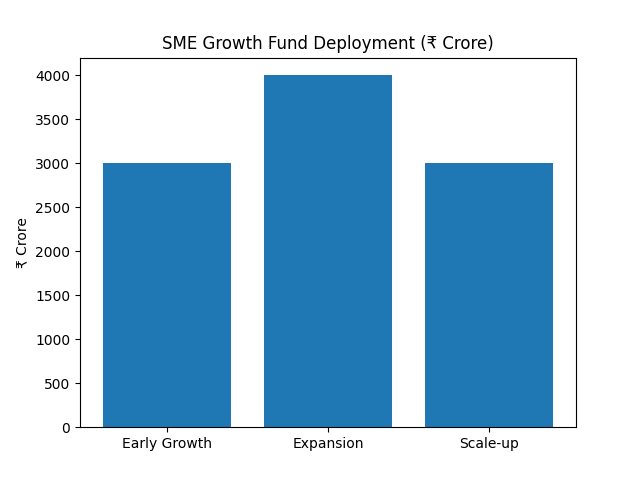
₹10,000 crore SME Growth Fund with performance-linked incentives
Support for municipal bond market development
REIT-based monetisation of underutilised CPSE real estate
Sectoral Impact:
MSMEs gain access to long-term growth capital
Financial markets deepen beyond traditional banking
Financial Markets & Investments: Depth, Liquidity, Stability
Capital Market Reforms:
Market-making framework for corporate bond indices
Introduction of derivatives and total return swaps on corporate bonds
Higher foreign portfolio investment limits for Persons Resident Outside India (PROI)
Securities Transaction Tax (STT) Changes:
- Futures STT increased to 0.05%
- Options premium STT raised to 0.15%
Investor Takeaway:
Encourages long-term investing over excessive short-term speculation
Direct Tax Reforms: Simplification & Trust-Based Compliance
Relief for Individuals & Small Taxpayers:
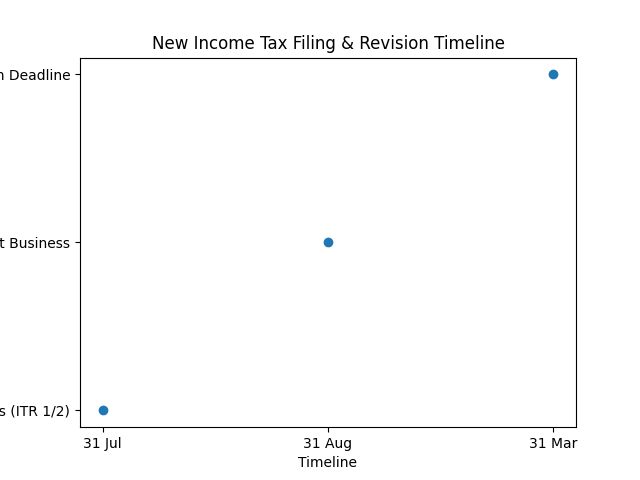
- Extended return revision deadline till 31 March
- Automated lower/nil TDS certificate system
- Reduced TCS on overseas education, medical & tour remittances (2%)
Foreign Asset Disclosure Scheme:
One-time compliance window with immunity from prosecution
Relief for small undisclosed foreign assets below ₹20 lakh
Corporate & International Taxation: Making India Competitive
MAT reduced to 14% and made final from April 2026
Buyback taxation shifted to capital gains
Tax holidays and safe harbour rules for:
Data centres
Cloud services
Non-resident experts
Why it matters:
- Improves India’s attractiveness as a global manufacturing and services hub
Trade & Customs: Supporting Domestic Value Addition
- Duty exemptions for critical minerals and capital goods
- Relief for seafood processing, footwear components, microwave ovens
- Continued customs relief for nuclear power projects till 2035
What This Budget Means for Investors
Long-Term Winners:
Infrastructure & railways
Electronics & semiconductors
Renewables & energy storage
Capital goods & logistics
Financial services (bonds, REITs)
Strategy Perspective:
This is not a trader’s budget, but a long-term investor’s roadmap focused on stability, scale, and structural reforms.
Final Thoughts
Union Budget 2026–27 reinforces India’s commitment to fiscal prudence, manufacturing self-reliance, and financial market depth. For investors and businesses alike, the message is clear: align with long-term themes rather than short-term noise.
From an investment perspective, this Union Budget 2026–27 Analysis confirms that India’s growth story will be driven by capital expenditure, manufacturing depth, and financial market maturity rather than short-term stimulus.
Frequently Asked Questions – Union Budget 2026–27 Analysis
Union Budget 2026–27 focuses on fiscal consolidation, infrastructure-led growth, domestic manufacturing, tax simplification, and long-term economic stability rather than short-term stimulus.
The budget supports long-term investment themes such as infrastructure, manufacturing, renewable energy, MSMEs, and bond markets, making it favorable for long-term investors.
Major tax changes include MAT reduction to 14%, simplified compliance for small taxpayers, buyback taxation under capital gains, reduced TCS on overseas remittances, and a foreign asset disclosure scheme.
The fiscal deficit for FY 2026–27 is estimated at 4.3% of GDP, continuing India’s path of fiscal consolidation while maintaining strong capital expenditure.
Key beneficiary sectors include infrastructure, railways, electronics, semiconductors, MSMEs, renewable energy, battery storage, and financial markets.
No. Union Budget 2026–27 discourages speculative trading and clearly favors long-term investment and capital formation.
The government announced a ₹10,000 crore SME Growth Fund to support early growth, expansion, and scale-up stages of promising SMEs through performance-linked incentives.
Disclaimer:
The information provided in this blog is for informational and educational purposes only and should not be construed as financial, investment, or legal advice. Equity investments are subject to market risks, and past performance is not indicative of future results.
This content does not constitute an offer, solicitation, or recommendation to buy or sell any securities, nor does it guarantee any specific financial outcome. Investors should conduct their own research, assess their risk tolerance, and consult with a certified financial advisor or investment professional before making any investment decisions.
The author and publisher of this blog are not liable for any financial losses, decisions, or actions taken based on the information provided. Invest wisely and at your own discretion.
